When conducting bioequivalence (BE) or bioavailability (BA) studies for regulatory approval, guidelines from different regulatory bodies must be adhered to. Here’s a summary of the key considerations and variations across major regulatory agencies
Regulatory Guidelines Comparison
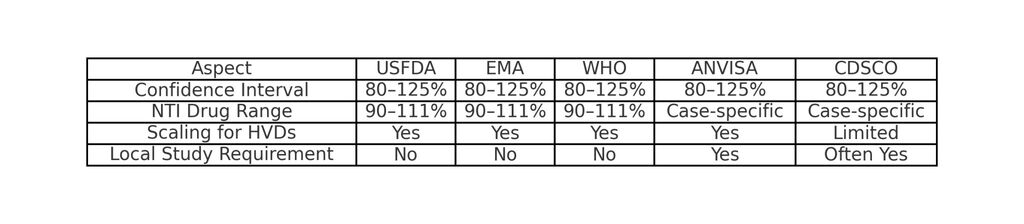
USFDA
- Focus: Bioequivalence for generic drug approval.
- Acceptance Range: 80–125% for Cmax and AUC with a 90% CI.
Special Cases:
- Highly variable drugs: Scaled bioequivalence approach.
- NTI drugs: Tighter limits (90–111.11%).
Study Design:
- Single-dose, fasting, or fed state based on product label.
- Population: Preferably 24–36 healthy volunteers, considering variability.
EMA
- Focus: Generics, biosimilars, and hybrid applications.
Acceptance Range:
- Standard: 80–125% (Cmax and AUC).
- Highly variable drugs: Widened limits for C_max (e.g., 75–133%).
- NTI drugs: Tighter range (90–111.11% for AUC).
Study Design:
- Single-dose fasting for IR
- Multiple-dose studies for modified-release forms.
- Fed State Studies: Required for food-dependent drugs.
WHO
- Focus: Global harmonization for generics in developing countries.
- Acceptance Range: 80–125% for C_max and AUC.
Study Design:
- Fasting state for immediate-release.
- Fed state for modified-release or food-dependent drugs.
- Special Considerations: Simplified requirements for essential medicines.
MHRA (UK)
- Adopts EMA guidelines with specific procedural adjustments.
- Additional Considerations: Local site-specific requirements for approval.
ANVISA (Brazil)
- Focus: Both national and imported generics.
- Acceptance Range: 80–125% for Cmax and AUC.
- Fed vs. Fasting: Both required for most products.
- Population: Ethnically diverse volunteers preferred.
- Local Data Requirement: Studies often need to be conducted in Brazil.
TGA (Australia)
- Adopts EMA standards but has independent review processes.
- Additional Guidance: Adjustments for Australian market-specific conditions.
CDSCO (India)
- Focus: Approvals for domestic and export generics.
- Guidelines: Based on USFDA and WHO but with local adaptations.
- Population: Often local volunteers for export markets.
- Clinical Trials Registry: Mandatory registration in India.
Special Drug Categories
- Highly Variable Drugs (HVDs): Scaling methods are accepted in many regions.
- NTI Drugs: Tighter ranges (90–111%).
- Modified-Release Products: Require fasting, fed, and steady-state studies.
Documentation Requirements
- Study protocol and report.
- Ethics committee approvals.
- Volunteer consent and demographic data.
- Pharmacokinetic analysis and statistical evaluations.
- Analytical method validation for drug quantification.
Practical Tips
- Always consult the latest regulatory guidance documents.
- Tailor study design to the target market.
- Engage with local CROs for region-specific compliance.
- Use bridging studies if submitting data to multiple agencies.
Summary
Read also:
- Reference Standard (RS) in Bioequivalence Studies
- Special BE Considerations for Highly Variable and Narrow Therapeutic Index Drugs
- Bioequivalence Study for Solid Oral Drug Products
Resource Person: Moinuddin syed. Ph.D, PMP®

